 Online Programming Server
Online Programming Server
Tutorial 105: Queue
You are here: Tutorials >> Basic >> Data Structures >> Queue
| Tutorial ID | 105 |
|---|---|
| Title | Queue |
In computer science, a queue is a particular kind of abstract data type or collection in which the entities in the collection are kept in order and the principal (or only) operations on the collection are the addition of entities to the rear terminal position and removal of entities from the front terminal position. This makes the queue a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure. In a FIFO data structure, the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed. This is equivalent to the requirement that once an element is added, all elements that were added before have to be removed before the new element can be invoked. A queue is an example of a linear data structure. Queues provide services in computer science, transport, and operations research where various entities such as data, objects, persons, or events are stored and held to be processed later. In these contexts, the queue performs the function of a buffer. Queues are common in computer programs, where they are implemented as data structures coupled with access routines, as an abstract data structure or in object-oriented languages as classes. Common implementations are circular buffers and linked lists. 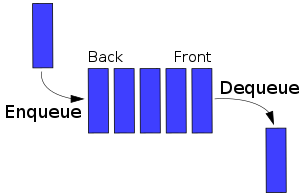 Queue implementation Theoretically, one characteristic of a queue is that it does not have a specific capacity. Regardless of how many elements are already contained, a new element can always be added. It can also be empty, at which point removing an element will be impossible until a new element has been added again. Fixed length arrays are limited in capacity, and inefficient because items need to be copied towards the head of the queue. However conceptually they are simple and work with early languages such as FORTRAN and BASIC which did not have pointers or objects. Most modern languages with objects or pointers can implement or come with libraries for dynamic lists. Such data structures may have not specified fixed capacity limit besides memory constraints. Queue overflow results from trying to add an element onto a full queue and queue underflow happens when trying to remove an element from an empty queue. A bounded queue is a queue limited to a fixed number of items. There are several efficient implementations of FIFO queues. An efficient implementation is one that can perform the operations—enqueuing and dequeuing—in O(1) time. Reference: Wikipedia | |
Related Problems
| problem_id | title | description | submit | accepted | difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1110 | Data Structure - Queue | Queue is a basic data structure. Read tutorial for more details. Your task is to implement a queue. | 0 | 0 | 110 |

Facebook