 Online Programming Server
Online Programming Server
Tutorial 104: Stack
You are here: Tutorials >> Basic >> Data Structures >> Stack
| Tutorial ID | 104 |
|---|---|
| Title | Stack |
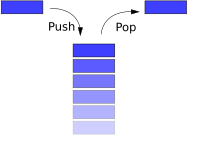
One way of describing the stack is as a last in, first out (LIFO) abstract data type and linear data structure. A stack can have any abstract data type as an element, but is characterized by two fundamental operations, called push and pop (or pull). The push operation adds a new item to the top of the stack, or initializes the stack if it is empty. If the stack is full and does not contain enough space to accept the given item, the stack is then considered to be in an overflow state. The pop operation removes an item from the top of the stack. A pop either reveals previously concealed items, or results in an empty stack, but if the stack is empty then it goes into underflow state (It means no items are present in stack to be removed). A stack pointer is the register which holds the value of the stack. The stack pointer always points to the top value of the stack.
(Image from http://www.algolist.net/Data_structures/Stack)ArrayThe array implementation aims to create an array where the first element (usually at the zero-offset) is the bottom. That is, typedef struct { size_t size; int items[STACKSIZE]; } STACK; The void push(STACK *ps, int x) { if (ps->size == STACKSIZE) { fputs("Error: stack overflow\n", stderr); abort(); } else ps->items[ps->size++] = x; } The int pop(STACK *ps) { if (ps->size == 0){ fputs("Error: stack underflow\n", stderr); abort(); } else return ps->items[--ps->size]; } If we use a dynamic array, then we can implement a stack that can grow or shrink as much as needed. The size of the stack is simply the size of the dynamic array. A dynamic array is a very efficient implementation of a stack, since adding items to or removing items from the end of a dynamic array is amortized O(1) time. | |
Related Problems
| problem_id | title | description | submit | accepted | difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1111 | Data Structure - Stack | Stack is a basic data structure. Read tutorial for more details. Your task is to implement a stack. | 1 | 0 | 235 |


Facebook